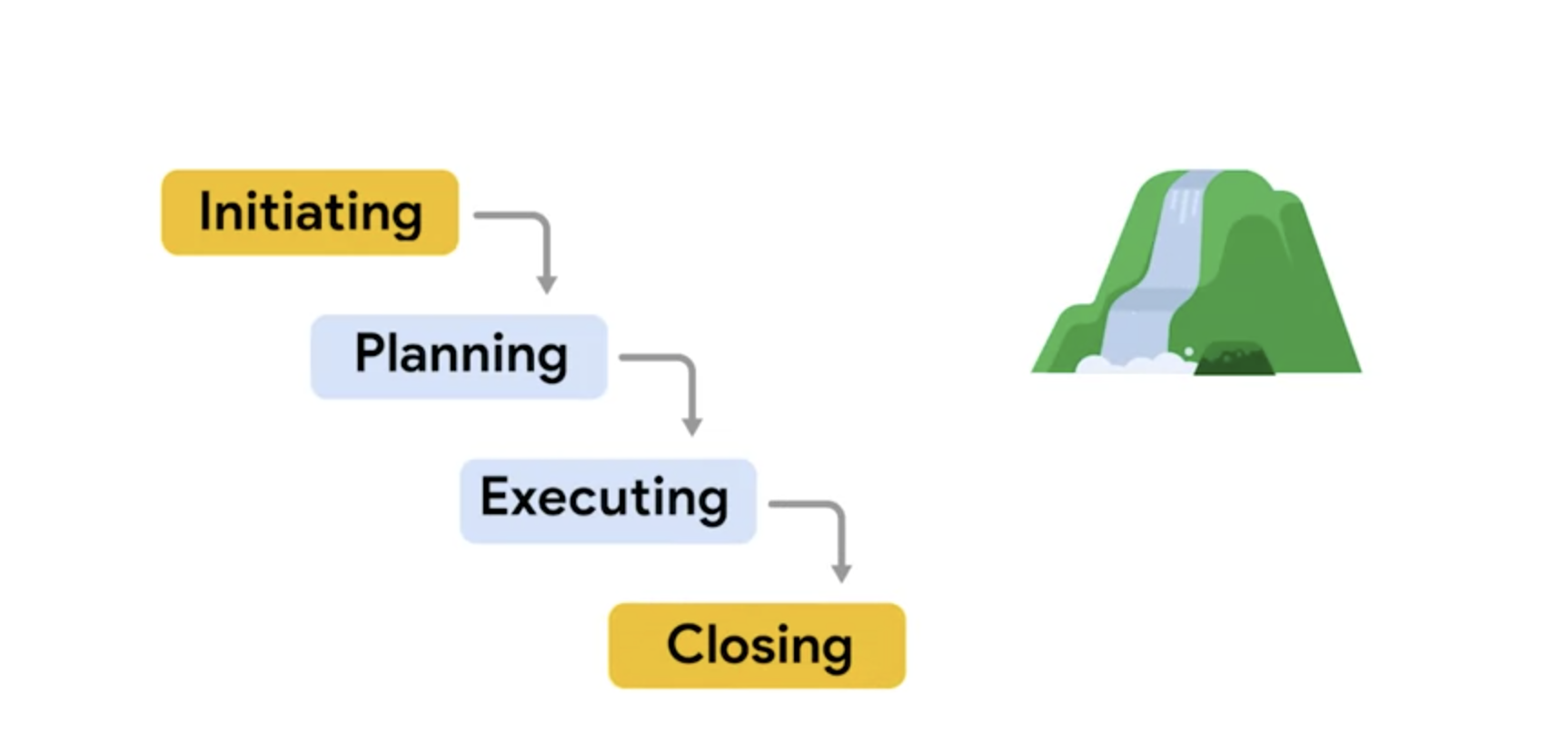
Now that you know more about some of the different approaches and frameworks associated with project management, let's compare specific aspects of Waterfall (also commonly called traditional) and Agile approaches.
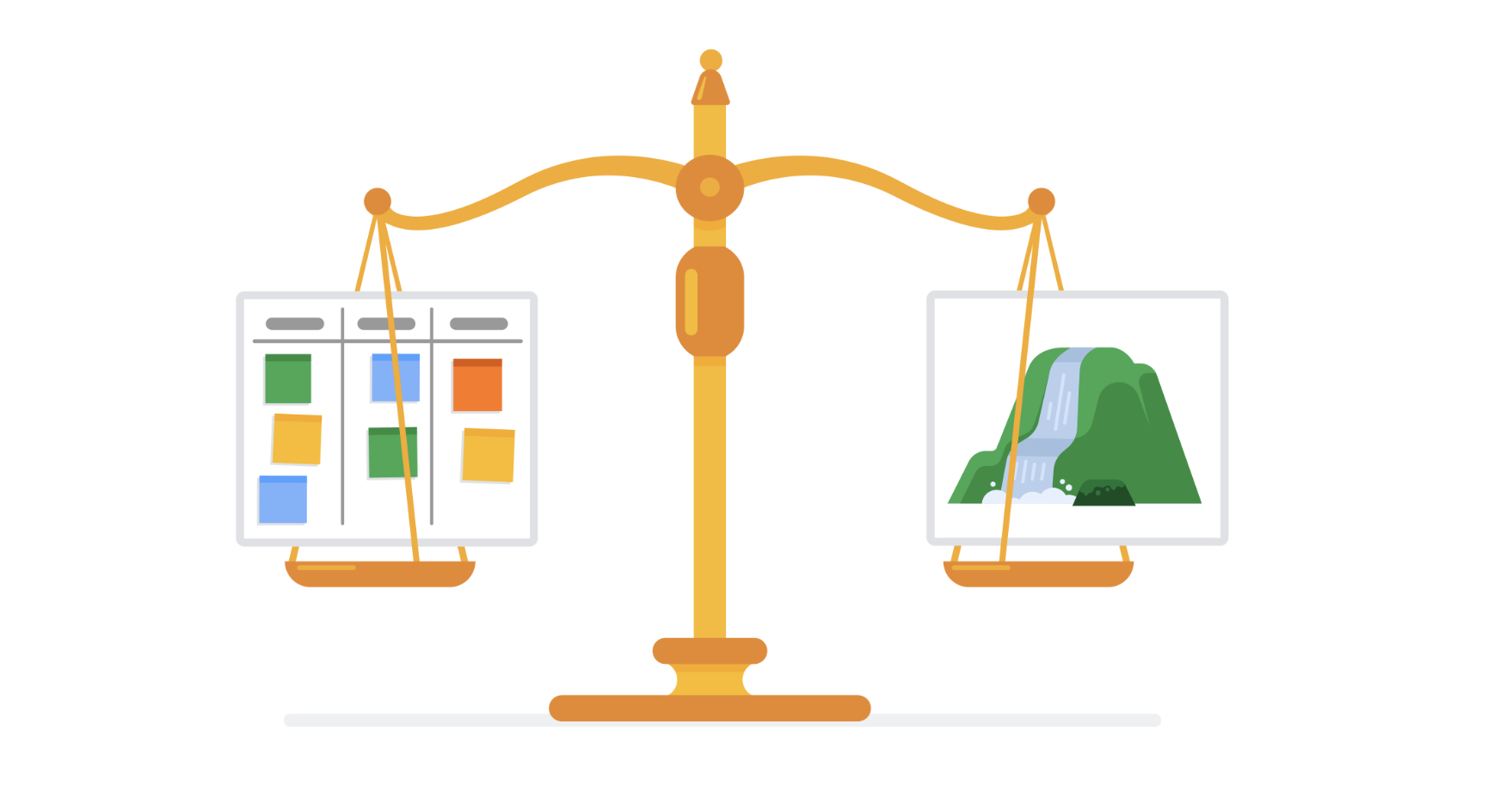 waterfall vs agile ilustrations // source image from coursera
waterfall vs agile ilustrations // source image from coursera
Understanding the fundamentals of—and differences between—these common project management approaches can help you demonstrate your project management knowledge during an interview. It can also help you evaluate a project to determine the right approach when working on the job.
Waterfall and Agile are implemented in many different ways on many different projects, and some projects may use aspects of each. The chart below briefly describes and compares Waterfall and Agile approaches. You can use it as a quick reference tool, but be aware that in practice, the differences between these two approaches may not always be clearly defined. Waterfall and Agile Comparison
| Waterfall | Agile | |
|---|---|---|
| Project manager's role | Project manager serves as an active leader by prioritizing and assigning tasks to team members. | Agile project manager (or Scrum Master) acts primarily as a facilitator, removing any barriers the team faces. Team shares more responsibility in managing their own work. |
| Scope | Project deliverables and plans are well-established and documented in the early stages of initiating and planning. Changes go through a formal change request process. | Planning happens in shorter iterations and focuses on delivering value quickly. Subsequent iterations are adjusted in response to feedback or unforeseen issues. |
| Schedule | Follows a mostly linear path through the initiating, planning, executing, and closing phases of the project. | Time is organized into phases called Sprints. Each Sprint has a defined duration, with a set list of deliverables planned at the start of the Sprint. |
| Cost | Costs are kept under control by careful estimation up front and close monitoring throughout the life cycle of the project. | Costs and schedule could change with each iteration. |
| Quality | Project manager makes plans and clearly defines criteria to measure quality at the beginning of the project. | Team solicits ongoing stakeholder input and user feedback by testing products in the field and regularly implementing improvements. |
| Communication | Project manager continually communicates progress toward milestones and other key indicators to stakeholders, ensuring that the project is on track to meet the customer’s expectations. | Team is customer-focused, with consistent communication between users and the project team. |
| Stakeholders | Project manager continually manages and monitors stakeholder engagement to ensure the project is on track. | Team frequently provides deliverables to stakeholders throughout the project. Progress toward milestones is dependent upon stakeholder feedback. |
Now that you better understand the differences between Waterfall and Agile project management approaches, you can use this understanding to determine which is most effective for your projects.
Others article:
- Flask Async Without Await - Part. 7 Belajar Flask Framework Untuk Pemula
- Hello world, membangun microservice dengan FastAPI
- FastAPI APIRouter, Membangun microservice dngan FastAPI
- Mini Wallet Bagian 1 - Django Template dan Static File
- Mini Wallet Bagian 2 - Django Template Base HTML
- Mini Wallet Bagian 3 - Dajngo Model dan Koneksi Database MySQL
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 1 - Create Read Update Delete
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 2 - Inner, Left, Right, Cross Join
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 3 - Filtering Data
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 4 - Grouping Data
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 5 - Operator dan Clausa
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 6 - Replace Statement
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 7 - Constraint Data
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 8 - Mengubah Struktur tabel
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 9 - Subquery
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 10 - Virtual Tabel
- Tutorial bassic Mysql bagian 11 - Control Flow Function
- Membuat service OTP bagian 1 - OTP dan PIN
- Membuat service OTP bagian 2 - Sequence Diagram
- Membuat service OTP bagian 3 - Model dan Serializer
- Membuat service OTP bagian 4 - Validate OTP
- Membuat service OTP bagian 5 - Api Client Service
- Membuat service user login bagian 1 - Konfigurasi Database
- Membuat service user login bagian 2 - Serializer dan JWT
- Membuat CRUD service product bagian 1 - Models Product
- Membuat CRUD service product bagian 2 - Function Serializer
- Membuat CRUD service product bagian 3 - Api Client Service
- Membaut CRUD service product bagian 4 - Auth User
- Membuat CRUD service product bagian 5 - TDR File Log
- Membuat CRUD service product bagian 6 - Unit Test
- Membuat service user register bagian 1 - Django
- Membuat Service user register bagian 2 - Django
- Membuat service filter dan download file CSV di django
- Django upload file menggunakan FileSystemStorage